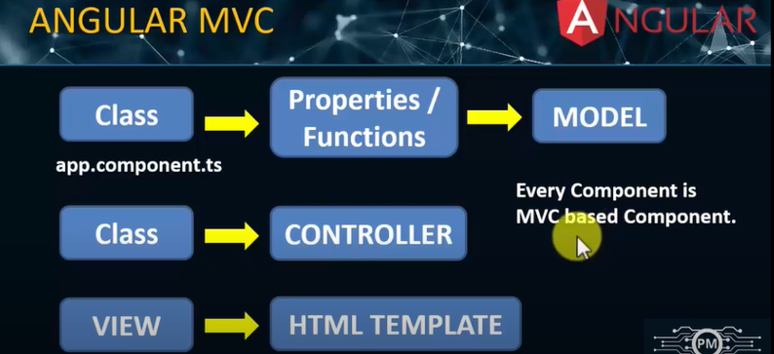
MVC (Model-View-Controller) is a software design pattern commonly used for developing web applications. It separates the application into three interconnected components:
- Model: Represents the data or business logic of the application.
- View: Represents the UI, displaying the data.
- Controller: Handles the input and updates the model and view.
Example of MVC in Angular
-
Controller (AppComponent)
TheAppComponentacts as the controller. It defines the logic and binds data from the model to the view.export class AppComponent { // Controller title = "Tutorial"; // Model (title is a property here) name = "Shoyeb"; // Model (name is a property here) } -
Model
Thetitleandnameproperties are part of the model, holding the data. -
View (app.component.html)
The HTML file is the view, where the data from the controller is displayed.<h1>{{ title }}</h1> <p>{{ name }}</p>
Key Points:
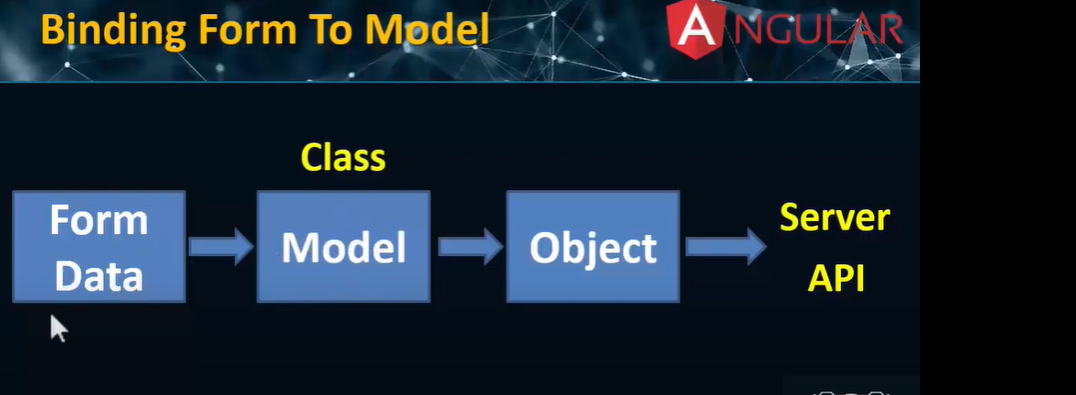
- The controller (
AppComponent) manages the data and updates the view (app.component.html). - The model consists of properties like
titleandnamein the component. - The view is where the user sees the data, and it’s updated when the model changes.