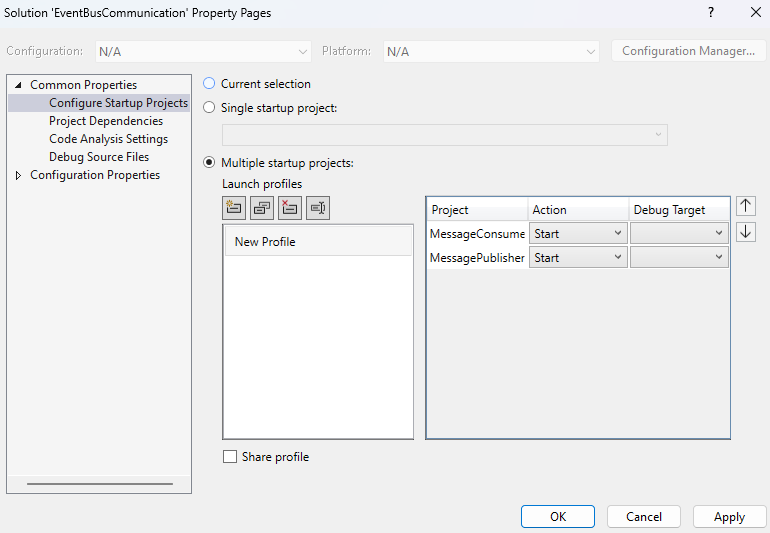
-
First, install Erlang from download, and then install RabbitMQ from download.
-
Navigate to the installation folder (
C:\Users\ASD\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\RabbitMQ Server) and run theRabbitMQ Service - startservice. Check if the service is running in Windows Services. -
Next, open the
RabbitMQ Command Prompt (sbin dir)and run the commandrabbitmq-plugins.bat enable rabbitmq_management.
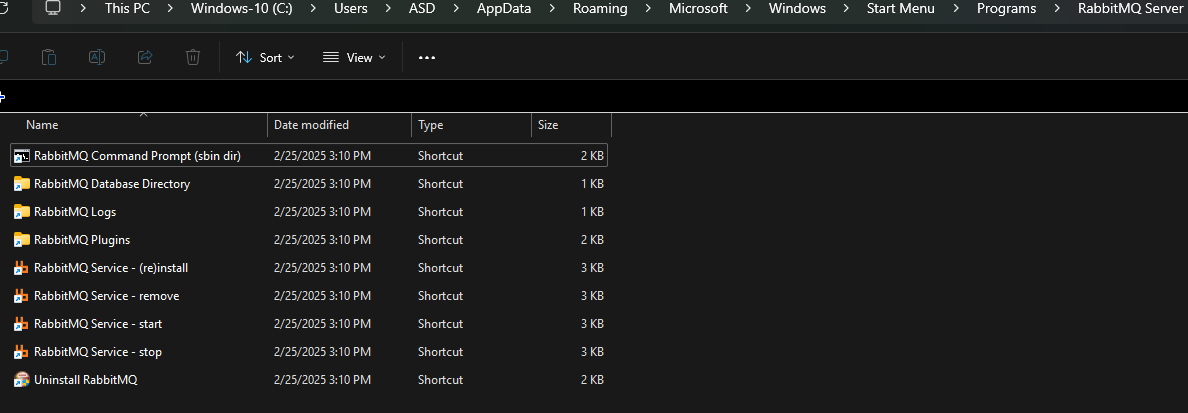
- Now, open the link
http://127.0.0.1:15672/and log in using the username and passwordguest.
(Alternatively, you can use Docker without installing Erlang and RabbitMQ clients. To do this, pull the RabbitMQ Docker image with docker pull rabbitmq:3.10-management and then run the RabbitMQ container using docker run -d --name rabbitmq -p 5672:5672 -p 15672:15672 rabbitmq:3-management. For more details, visit Rabbitmq docker setup guide).
Event Bus Architecture
For more information on the Event Bus architecture, check out this article: efficient-event-communication-implementing-event-bus-and-outbox-patterns-with-cap-in-net-core-microservices
- First, create a new blank solution, and then add two API projects beneath it named
MessagePublisherandMessageConsumer. Afterward,
For MessagePublisher Project:
-
Install the following NuGet packages in publisher projects:
DotNetCore.CAPDotNetCore.CAP.DashboardDotNetCore.CAP.RabbitMQDotNetCore.CAP.SqlServerMicrosoft.AspNetCore.OpenApiMicrosoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServerMicrosoft.EntityFrameworkCoreMicrosoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools
Or, you can install them all at once by adding the following to your
.csprojfile:<ItemGroup> <PackageReference Include="DotNetCore.CAP" Version="8.3.3" /> <PackageReference Include="DotNetCore.CAP.Dashboard" Version="8.3.3" /> <PackageReference Include="DotNetCore.CAP.RabbitMQ" Version="8.3.3" /> <PackageReference Include="DotNetCore.CAP.SqlServer" Version="8.3.3" /> <PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore" Version="9.0.2" /> <PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer" Version="9.0.2" /> <PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools" Version="9.0.2"> <PrivateAssets>all</PrivateAssets> <IncludeAssets>runtime; build; native; contentfiles; analyzers; buildtransitive</IncludeAssets> </PackageReference> <PackageReference Include="Swashbuckle.AspNetCore" Version="6.6.2" /> </ItemGroup> -
Add an entity named
Customer:
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace MessagePublisher.Entities
{
public class Customer : CustomerInsert
{
[Key]
public int Id { get; set; }
}
public class CustomerInsert
{
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public string MobilNumber { get; set; }
}
}- Now add a Service class named
CustomerServiceand its interfaceICustomerService:
public interface ICustomerService
{
Task<bool> AddCustomer(CustomerInsert order);
}public class CustomerService : ICustomerService
{
private readonly ServiceDbContext _dbContext;
private readonly ICapPublisher _capPublisher;
public CustomerService(ServiceDbContext dbContext, ICapPublisher capPublisher)
{
this._dbContext = dbContext;
_capPublisher = capPublisher;
}
public async Task<bool> AddCustomer(CustomerInsert customerInsert)
{
Customer customer = new Customer
{
FirstName = customerInsert.FirstName,
LastName = customerInsert.LastName,
MobilNumber = customerInsert.MobilNumber,
};
await _dbContext.AddAsync(customer);
await _dbContext.SaveChangesAsync();
var content = JsonSerializer.Serialize(customer);
await _capPublisher.PublishAsync<string>("CustomerAdded", content);
return true;
}
}- Now add an API-based controller named
CustomerController:
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class CustomerController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly ICustomerService _customerService;
public CustomerController(ICustomerService customerService)
{
_customerService = customerService;
}
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> Post([FromBody] CustomerInsert customer)
{
try
{
return Ok(await _customerService.AddCustomer(customer));
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw;
}
}
}- Add a DbContext name
ServiceDbContext
public class ServiceDbContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Customer> Customers { get; set; }
public ServiceDbContext(DbContextOptions<ServiceDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
}
}- Add a line into
appsetting.json
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "Server=.\\SQLEXPRESS; Database=EventBusDB; Trusted_Connection=True; TrustServerCertificate=True;"
}- Modify
program.cs
// DBContext
builder.Services.AddDbContext<ServiceDbContext>(options => options.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection")));
// RabbitMQ Setup
builder.Services.AddCap(options =>
{
options.UseEntityFramework<ServiceDbContext>();
options.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection"));
options.UseDashboard(path => path.PathMatch = "/cap-dashboard");
options.UseRabbitMQ(options =>
{
options.ConnectionFactoryOptions = options =>
{
options.Ssl.Enabled = false;
options.HostName = "localhost";
options.UserName = "guest";
options.Password = "guest";
options.Port = 5672;
};
});
});
/// Service
builder.Services.AddScoped<ICustomerService, CustomerService>();-
Apply the migration only to the
Publisherproject by running:dotnet ef migrations add InitialCreate dotnet ef database update(Make sure the
dotnet-eftool is installed globally with[dotnet tool install --global dotnet-ef]).
For MessageConsumer Project:
-
Install the following NuGet packages in consumer projects:
-
DotNetCore.CAP -
DotNetCore.CAP.Dashboard -
DotNetCore.CAP.RabbitMQ -
DotNetCore.CAP.SqlServer -
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
Or, you can install them all at once by adding the following to your
.csprojfile:<ItemGroup> <PackageReference Include="DotNetCore.CAP" Version="8.3.3" /> <PackageReference Include="DotNetCore.CAP.Dashboard" Version="8.3.3" /> <PackageReference Include="DotNetCore.CAP.RabbitMQ" Version="8.3.3" /> <PackageReference Include="DotNetCore.CAP.SqlServer" Version="8.3.3" /> <PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer" Version="9.0.2" /> <PackageReference Include="Swashbuckle.AspNetCore" Version="6.6.2" /> -
- Add a subscriber named
CustomerAddedEventSubscriber:
public class CustomerAddedEventSubscriber : ICapSubscribe
{
[CapSubscribe("CustomerAdded")]
public void Consumer(JsonElement customerData)
{
Console.WriteLine(customerData);
}
}- Add a DbContext named
MainDbContext
public class MainDbContext : DbContext
{
public MainDbContext(DbContextOptions<MainDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
}
}- Add a line into
appsetting.json
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "Server=.\\SQLEXPRESS; Database=TempoDB; Trusted_Connection=True; TrustServerCertificate=True;"
}- Modify in
program.cs
// DbContext
builder.Services.AddDbContext<MainDbContext>(options => options.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection")));
// Cap Setup
builder.Services.AddCap(options =>
{
options.UseEntityFramework<MainDbContext>();
options.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection"));
options.UseDashboard(path => path.PathMatch = "/cap-dashboard");
options.UseRabbitMQ(options =>
{
options.ConnectionFactoryOptions = options =>
{
options.Ssl.Enabled = false;
options.HostName = "localhost";
options.UserName = "guest";
options.Password = "guest";
options.Port = 5672;
};
});
});
// Event Handler Service
builder.Services.AddSingleton<CustomerAddedEventSubscriber>();- After starting both projects at the same time, two CAP tables will be automatically generated:
cap.Publishedandcap.Received. If there are two different databases, it will create two differentcap.Publishedandcap.Receivedtables on each database. To view the dashboard in each project, visithttp://localhost:xxxx/cap-dashboard.